本文是《Solr In Action》读书笔记,包含第1~2章
Chapter 01. Introduction to Solr
What’s Solr
Apache Solr, is a specific NoSQL technology.
Solr is a scalable, ready-to-deploy enterprise search engine that’s optimized to search large volumes of text-centric data and return results sorted by relevance.
Scalable— Solr scales by distributing work (indexing and query processing) to multiple servers in a cluster.Ready to deploy— Solr is open source, is easy to install and configure, and provides a preconfigured example to help you get started.Optimized for search— Solr is fast and can execute complex queries in subsecond speed, often only tens of milliseconds.Large volumes of documents— Solr is designed to deal with indexes containing many millions of documents.Text-centric— Solr is optimized for searching natural-language text, like emails, web pages, resumes, PDF documents, and social messages such as tweets or blogs.Results sorted by relevance— Solr returns documents in ranked order based on how relevant each document is to the user’s query.
Solr is:
Information retrieval engine inverted index; ranking documents by relevance
Flexible schema management xml-configuration
Java web application REST-like services
Multiple indexes in one server data partitioning
Extendable (plugins) Each subsystem (document management; query processing; text analysis) is composed of a modular “pipeline” that allows you to plug in new functionality
Scalable Provides flexible cache-management features.
Query throughput: addreplicasof your index so that more servers can handle more requests.
The number of documents indexed: split the index into smaller chunks calledshards, then distribute the searches across the shards.Fault-tolerant
Solr适合处理哪种数据
Solr are optimized to handle data exhibiting four main characteristics:
- Text-centric Text-centric data implies that the text of a document contains information that users are interested in finding.
- Read- dominant Think of read-dominant as meaning that documents are read far more often than they’re created or updated.
- Document-oriented In a search engine, a document is a self-contained collection of fields, in which each field only holds data and doesn’t contain nested fields. (FLAT structure)
- Flexible schema This means that documents in a search index don’t need to have a uniform structure.
Features
User-experience features
Pagination and sortingFaceting: category search results into subgroups.AutosuggestSpell checkerHit highlightingGeospatial search
Data-modeling features
Result grouping /field collapsing. 不同于facet: allows you to return unique groups instead of individual documents in the resultsFlexible query supportJoins: like sql subqueryDocument clustering: identify groups of documents that are similarImport rich document formats: pdf, wordImport relational databasesMultilingual support
New features in Solr4
Near real-time search: be searchable within seconds of being added to the index.Atomic updates with optimistic concurrency: Solr uses a special version field named version to enforce safe update semantics for documents.Real-time get: ?Write durability using a transaction log: can control when to commit documents to make them visible in search results without risking data loss if a server fails before you commit.Easy sharding and replication using ZooKeeper: uses Apache ZooKeeper to distribute configurations and manage shard leaders and replicas
Compare
Solr vs. Lucene
- Lucene provides the library for indexing documents and executing queries.
- With Lucene, you need to write Java code to define fields and how to analyze those fields.
- Solr uses
schema.xmlto represent all of the possible fields and data types necessary to map documents into a Lucene index. - Solr also adds nice constructs on top of the core Lucene indexing functionality (
copy fieldanddynamic field).
Lucene provides a powerful library for indexing documents, executing queries, and ranking results. And, with schema.xml, you have a flexible way to define the index structure using an XML-configuration document instead of having to program to the Lucene API.
Solr vs. MapReduce
- The need to build a web-scale
inverted indexled to the invention of MapReduce. - The map phase produces a unique term and document ID where the term occurs.
- In the reduce phase, terms are sorted so that all term/docID pairs are sent to the same reducer process for each unique term. The reducer sums up all term frequencies for each term to generate the inverted index.
Apache
Hadoopprovides an open source implementation ofMapReduce, and it’s used by the ApacheNutchopen source project to build aLuceneinverted index for web-scale search usingSolr.
Solr vs. SolrCloud
- SolrCloud is the code name for a subset of features in Solr 4 that makes it easier to configure and run a scalable, fault-tolerant cluster of Solr servers.
- Think of SolrCloud as a way to configure a distributed installation of Solr 4.
Chapter 02. Getting to know Solr
Query 参数
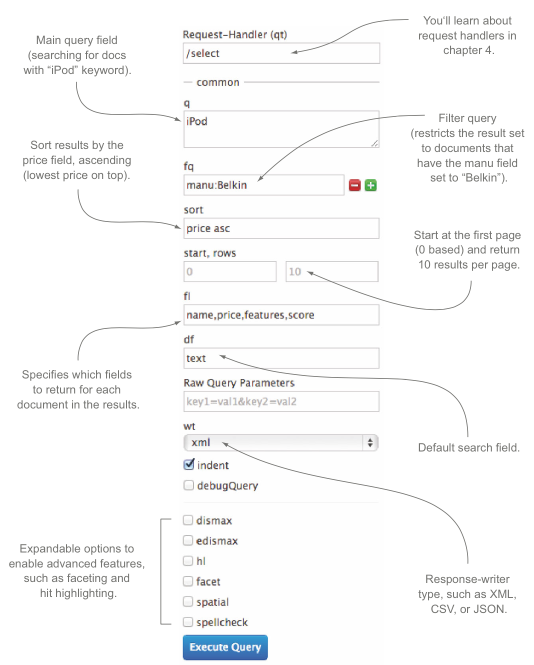
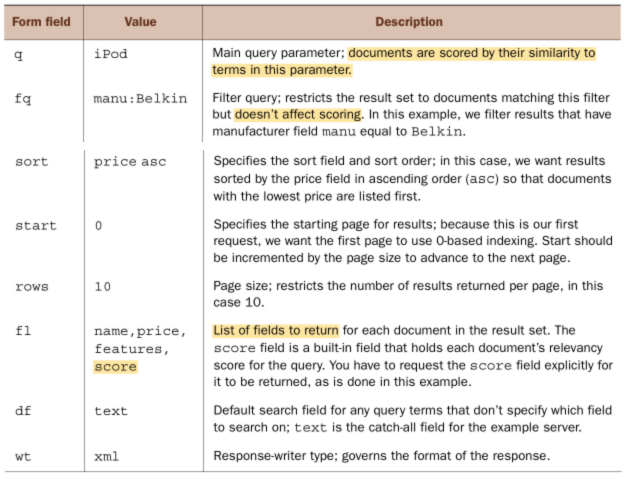
Filter query: restricts the result set to documents matching this filter but doesn’t affect scoring.start, rows: 用于分页。 the underlying Lucene index isn’t optimized for returning many documents at once.
in comparison to query execution, results construction is a slow process.
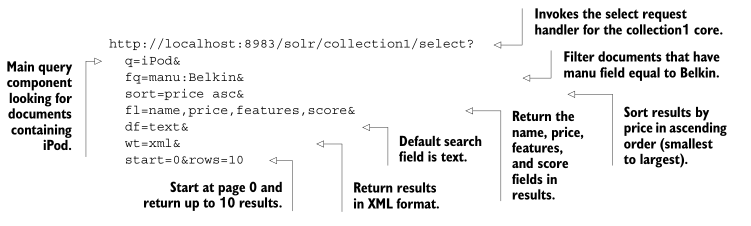
When you fill out the query form, an HTTP GET request is created and sent to Solr.
对应的HTTP Get请求:
返回参数
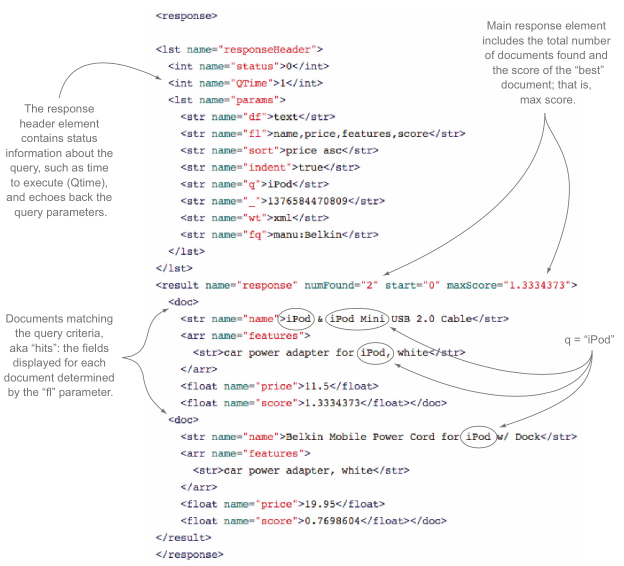 返回结果是按照score排序的:Ranked retrieval。
除非指定了sort参数。
返回结果是按照score排序的:Ranked retrieval。
除非指定了sort参数。
Solritas
Solr prov ides a customizable example search UI, called Solritas, to help you prototype your own awesome search application. http://localhost:8983/solr/collection1/browse