本文是《Solr In Action》读书笔记,包含第3章
Chpater 03. Key Solr Concepts
Basic
Document:
A document is a collection of fields that map to particular field types defined in a schema.
Solr is a document storage and retrieval engine. Every piece of data submitted to Solr for processing is a document.
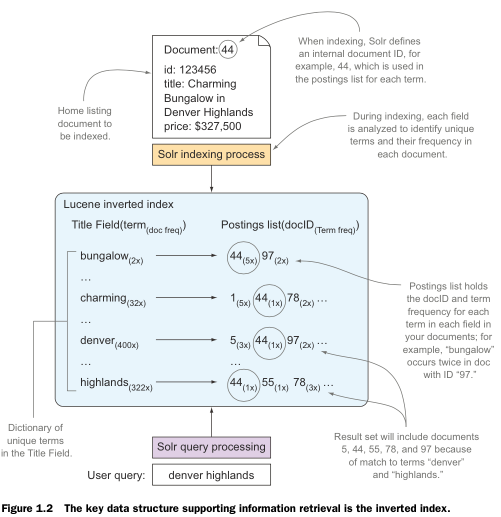
Inverted index:
Maps each word/term in the corpus to all of the documents in which it appears.
determin textually similar words, understand synonyms, remove unimportant words, score each result… Solr accomplishes all of this by using an index that maps content to documents instead of mapping documents to content as in a traditional database model.
Query
通过Inverted Index,可以实现如下查询:
Required Terms: new AND house; +new +houseOptional Terms: new house; new OR house. (default)Negated Terms: new house NOT rental; new house -rentalPhrases: “new home” OR “new house”Grouped expressions: New AND (house OR home)
为了支持Phrase查询:
Term Position: recording of the relative position of terms within a document. can tell us where in the document each term appears.存储在inverted index中,可用于支持
Phrase查询。
Fuzzy matching
Fuzzy matching is defined as the ability to perform inexact matches on terms in the search index. For example,
Wildcard searching
search for any words that start with a particular prefix.
1 2 3 | |
注意:
- the more characters you specify at the beginning of the term before the wildcard, the faster the query should run.
- 执行
leading wildcard(*ing)会很耗时,可以通过ReversedWildcardFilterFactory来解决,不过这样会增加index时间,并减慢整体查询速度。
Range searching
1 2 | |
Fuzzy searching/Edit-distance searching
find spelling variations within one or two characters (handle spelling errors).
1 2 | |
Solr provides the ability to handle character variations using edit-distance measurements based upon Damerau-Levenshtein distances, which account for more than 80% of all human misspellings.
An
edit distanceis defined as an insertion, a deletion, a substitution, or a transposition of characters.
Proximity searching
match two terms within some maximum distance of each other. e.g. search:
1
| |
改进:
1
| |
Solr内部用tem positions来计算edit distance.
Relevancy
Solr calculaes a relevancy score for each document and then sorting the search results from the high- est score to the lowest.
Similarity
【Q】那么relevancy score是如何计算的?受哪些因素的影响呢?
【A】Similarity:
- Solr’s relevancy scores are based upon the
Similarityclass, which can be defined on a per-field basis in Solr’sschema.xml. Similarityis a Java class that defines how a relevancy score is calculated based upon the results of a query.
实现原理:two-pass model
- First, it makes use of a
Boolean modelto filter out any documents that do not match the customer’s query. - Then it uses a
vector space modelfor scoring and drawing the query as a vector, as well as an additional vector for each document. - The similarity score for each document is based upon the
cosinebetween the query vector and that document’s vector.
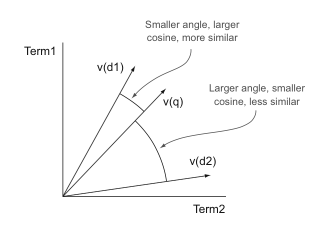
【Q】显然,重点是如何算出合理的vector?
【A】算法如下:

- term frequency (
tf), - inverse document frequency (
idf), - term boosts (
t.getBoost), - field normalization (
norm), - coordination factor (
coord), - query normalization (
queryNorm)
Term Frequency
Term frequency (tf)is a measure of how often a particular term appears in a matching document.- The more times the search term appears within a document, the more relevant that document is considered.
并非线性关系;而用了平方根。见上图。
Inverse Document Frequency
Inverse document frequency (idf), a measure of how “rare” a search term is, is calcu- lated by finding the document frequency (how many total documents the search term appears within), and calculating its inverse.Term frequencyandinverse document frequency, when multiplied together in the relevancy calculation, provide a nice counterbalance :- The
term frequencyelevates terms that appear multiple times within a document, - whereas the
inverse document frequencypenalizes those terms that appear commonly across many documents.作用:减少common words对评分的影响。
Boosting
If you have domain knowledge about your content—you know that certain fields or terms are more (or less) important than others—you can supply boosts at either indexing time or query time to ensure that the weights of those fields or terms are adjusted accordingly.
- Query-time boosting
1 2 | |
- Index-time boosting
it’s possible to boost documents or fields within documents at index time
Filed Normalization
The default Solr relevancy formula calculates three kinds of normalization factors (norms):
field norms,query norms, and thecoord factor.
- The
field normalization factor (field norm)is a combination of factors describing the importance of a particular field on a per-document basis.
This byte packs a lot of information:
- the boost set on the document when indexed,
- the boost set on the field when indexed,
- and a length normalization factor that penalizes longer documents and helps shorter documents
Query Normalization
Query Norm does not affect the overall relevancy ordering, as the same queryNorm is applied to all documents.
It merely serves as a normalization factor to attempt to make scores between queries comparable.
The Coord Factor
Its role is to measure how much of the query each document matches.
Precision and Recall
Precision:
1
| |
- Precision is a measure of how “good” each of the results of a query is,
- but it pays no attention to how thorough it is; *a query that returns one single correct doc- ument out of a million other correct documents is still considered perfectly precise. *
- Precision is answering the question: “Were the documents that came back the ones I was looking for?”
Recall
1
| |
- Recall is a measure of how thorough the search results are.
- Recall is answering the question: “How many of the correct documents were returned?”
区别:
- Precision is high when the results returned are correct; Recall is high when the correct results are present.
- Recall does not care that all of the results are correct. Precision does not care that all of the results are present.
平衡:
- measuring for
Recallacross the entire result set; - measuring for
Precisiononly within the first page (or few pages) of search results.
Searching at Scale
Solr is able to scale to handle billions of documents and an infinite number of queries by adding servers.
The denormalized document
- A
denormalized documentis one in which all fields are self-contained within the document, even if the values in those fields are duplicated across many documents. - 优点:extreme scalability. Because we can make the assumption that each document is self-contained(自包含), this means that we can also partition documents across multiple servers without having to keep related documents on the same server (because documents are independent of one another)
- 不同document的字段值会有重复。
- 与传统关系数据库不一样!
Distributed Searching
- sometimes your search servers may become overloaded by either too many queries at a time or by too much data needing to be searched through for a single server to handle.
- 后一种情况的解决办法:aggregated search:
1 2 3 | |
- distributed search across multiple Solr cores is run in parallel on each of those index partitions
即:
partition,shard;将大量的数据分区到不同的core,然后通过aggregated search并行地同时在这些core上进行查询。
Clusters vs. Servers
- the servers for this use case are mutually dependent. If one becomes unavailable for searching, they all become unavailable for searching and begin failing
- 上例中,如果box2服务器挂掉,返回结果就会报错。
- Solr provides excellent built-in cluster-management capabilities through the use of Apache ZooKeeper
Limits
- Solr is NOT relational in any way across documents. It’s not well suited for joining significant amounts of data across different fields on different documents, and it can’t perform join operations at all across multiple servers.
- The denormalized nature of Solr can be particularly problematic when the data in one field that is shared across many documents changes
you can insert, delete, and update documents, but not sin- gle fields (easily).
whenever a new field is added to Solr or the contents of an existing field have changed, every single document in the Solr index must be reprocessed in its entirety before the data will be populated for the new field in all documents.
Solr is not optimized for processing quite long queries (thousands of terms) or returning quite large result sets to users.
- elastic scalability: the ability to automatically add and remove servers and redistribute content to handle load.