下图展示了JVM的主要结构:
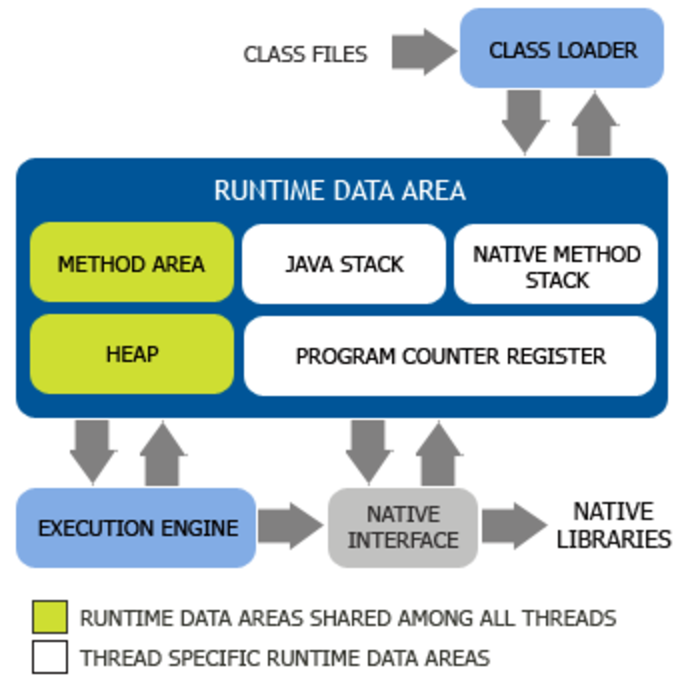
可以看出,JVM主要由以下几部分组成: - 类加载器子系统 - 运行时数据区(内存空间) - 执行引擎 - 本地方法接口
运行时数据区又分为: 1. 程序计数器 2. Java栈 3. 本地方法栈 4. 方法区 5. 堆
下图展示了JVM的主要结构:

可以看出,JVM主要由以下几部分组成: - 类加载器子系统 - 运行时数据区(内存空间) - 执行引擎 - 本地方法接口
运行时数据区又分为: 1. 程序计数器 2. Java栈 3. 本地方法栈 4. 方法区 5. 堆
Please ref to the demo code:
git clone https://github.com/AlphaWang/guava-demo.git
The Guava library has its history rooted in working with collections, starting out as google-collections. The Google Collections Library has long since been abandoned, and all the functionality from the original library has been merged into Guava.
Please ref to the demo code:
git clone https://github.com/AlphaWang/guava-demo.git
Many of Guava’s utilities are designed to fail fast in the presence of null rather than allow nulls to be used.
com.alphawang.guava.ch1.optional.Test1_FailFast
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
Additionally, Guava provides a number of facilities both to make using null easier, when you must, and to help you avoid using null.
本文是《Solr In Action》读书笔记,包含第3章
本文是《Solr In Action》读书笔记,包含第1~2章
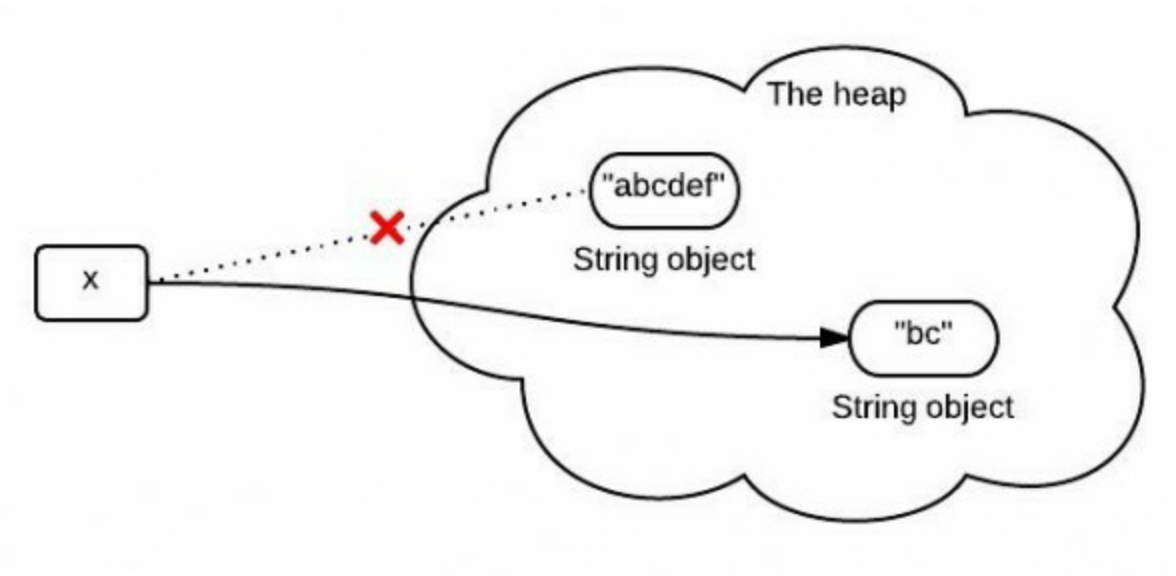
String#substring()在Java6和Java7中的实现是不一样的。这是因为Java6的实现可能导致内存问题,所以Java7中为了改善这个问题修改了实现方式。那么Java7中的实现就真的合理吗?
首先让我们来猜测一下,Java是如何实现substring功能的。由于String是不可变的,可能我们会猜测实现机制如下图:
支持switch字符串是Java7增加的一个新特性,那么它的底层是如何实现的呢?我们来看一个switch String的例子,然后分析编译器是如何处理的。
Java语言中有8种基本类型和一种比较特殊的类型String。为了使这些类型在运行过程中速度更快,更节省内存,都提供了一种常量池的概念。常量池就类似一个Java系统级别提供的缓存。
其中8种基本类型的常量池都是系统协调的,而String类型的常量池比较特殊。它的主要使用方法有两种:
String对象会直接存储在常量池中。String对象,可以使用String.intern()方法。intern方法会从字符串常量池中查询当前字符串是否存在,若不存在就会将当前字符串放入常量池中本文记录了一些Java源码中的良好编程习惯、运用的设计模式。
本文记录了一些Java源码中设计不合理之处、违反设计模式之处,以及其他可以改进的地方。